Counter concept
In many applications, the recording of consumed or generated quantities plays a central role. We distinguish between two formats for recording and evaluation:
Power/Throughput: In order to know which quantity is currently being consumed or generated, a representation in quantity per hour is used. For a water meter this would be the flow rate in m³/h and for an electricity meter the power in kWh/h or kW for short. This value can be read from some measuring instruments, but it can also be calculated by analyzing the meter readings over time.
Consumption/Generation (work) To calculate which quantity has been consumed or generated in a certain period (e.g. day, week, month), power/throughput values or counter values can be used. The latter are significantly more accurate, even if sampling rate of the data is lower.
AnyViz handles both power to work and work to power conversions. Thus, one tag can be used for both evaluation purposes. However, the conversion from power to work is much less accurate. Thus, the recording of counter values is recommended.
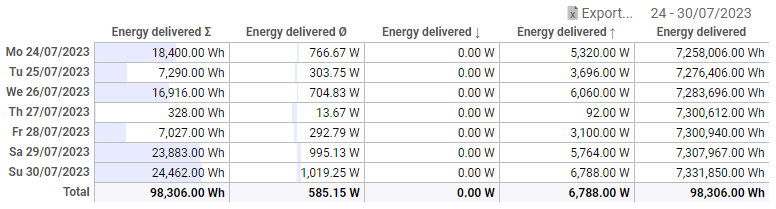
Example: Energy meter
In the following example, a counter tag 'Energy delivered' has been created to record the meter reading of energy. Using the pivot vizual, this tag can be evaluated in 5 different ways:
- Sum: The amount of energy (work) in Wh
- Average: The average power in W
- Min: The minimum power in W
- Max: The maximum power in W
- Current count: The counter reading at the beginning of the day in kWh
Switching the unit is done automatically in some constellations. To specify the unit for consumption/generation and power/throughput, both variants are separated by a semicolon in the Unit field of the tag editor.
Note: The counter concept can be applied to many areas. E.g. to record the produced quantity of a final product, the consumption of water, quantity of sorted out parts, etc.
Meter overflow
During an overflow or replacement of a meter, the meter reading drops to a lower value and grows again. AnyViz automatically detects this, ignores falling meter readings, and continues calculations when values increase.
Between the maximum meter value and the new starting value, no amount can be determined. Therefore, for a planned overflow or replacement, it is important to ensure the new starting value is recorded before amounts are consumed/delivered.
Manual meter interruption
In rare cases, the replacement meter starts with a higher meter reading than the previous meter. For AnyViz to interrupt amount calculations, a meter replacement must be entered manually. To do this, click on Add in the tag information. The timestamp must be between the last value of the old meter and before the first value of the new meter.